
GraphQL in Spring boot(二) Mutation 與 Scalar Type
上一篇講到了基本的 GraphQL 的 Query 操作以及 Field Resolver 的用法,本篇就來談談對資料進行修改用的 Mutation,以及自定義基本型態,在 GraphQL 也被稱為 Scalar Type
沒看過前一篇的可以點這邊:
Mutation
上一篇提到 Query 是用來取得資料的,而 Mutation 就是負責資料的修改,包含新增、修改、刪除,其實沒什麼特別的就直接看到實作吧
- Schema 的寫法:
type Mutation{
createPost(content:String!, authorId:Int!): Post
}
- Mutation 實作
@Component
@Slf4j
public class PostMutation implements GraphQLMutationResolver {
@Autowired
private PostDaoService postDaoService;
public Post createPost(String content, Long authorId) {
PostDto postDto = new PostDto();
postDto.setContent(content);
postDto.setAuthorId(authorId);
return postDaoService.create(postDto);
}
}
- 實際測試:
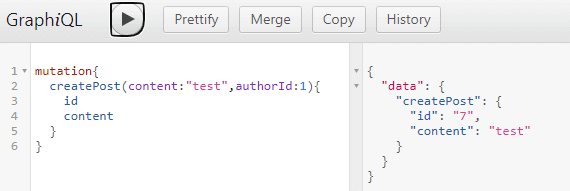
回傳一樣可以指定想要的結構,這樣看來其實跟 Query 的部分沒什麼區別,甚至將資料的更動寫在 Query 的 operation 都可以,反正實作都隨自己高興,算是一種規範而已
Input
當需求用到建立或是修改資料的時候,難免會要傳入大量的資料欄位,這時候如果一個參數一個參數的寫,一方面可讀性很差,一方面在實作的時候也不太好使用,所以 GraphQL 也有提供傳入 Object input 的方法,只不過需要透過新的關鍵字 input
- 像這樣用
input宣告一個專門用來輸入的 Object,就可以帶入到 Mutation 的輸入參數了
input PostCreateInput{
content: String
authorId: ID
}
type Mutation{
createPost(postCreateInput:PostCreateInput): Post
}
- 實作上就是把輸入換成物件而已,這邊順便還加上了資料驗證的功能,前幾篇有介紹過看這
@Component
@Slf4j
@Validated
public class PostMutation implements GraphQLMutationResolver {
@Autowired
private PostDaoService postDaoService;
public Post createPost(@Valid PostDto postCreateInput) {
return postDaoService.create(postCreateInput);
}
}
- 使用上帶入完整的物件結構
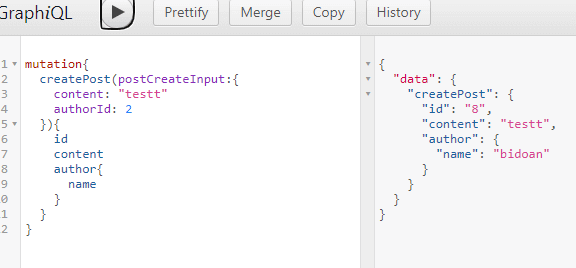
- 驗證失敗會像下面
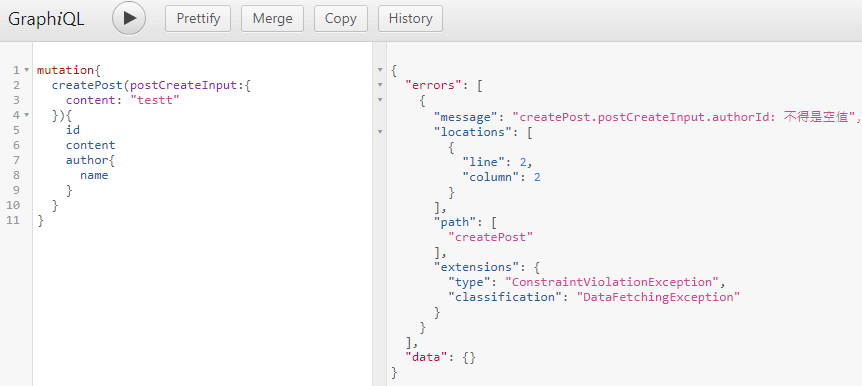
這邊錯誤訊息其實還是希望能夠經過 ExceptionHandler 回傳正確的 Http 的狀態,目前看起來不論怎麼拋出異常都是回傳 200,這部分需要再研究一下
Scalar Type
Scalar Type 指的是 GraphQL 的基本型別,預設總共有五個
- Int
- Float
- String
- Boolean
- ID
Scalar Type 的用意在於對資料的型態驗證,也就是不能把字串填到 Int 的欄位這樣的情境
而 ID 前一篇也有提到,雖然是基本型別但是卻不算有驗證功能,主要是給人看的
Custom Scalar Type
雖說 Scalar Type 可以用來做第一步的資料驗證,但是光只有數字跟字串的檢查實在有點不足,因此 GraphQL 還有提供客製化 Scalar Type 的功能,可以自定義基本的資料類型來進行處理,常見的像是: URL、Date、Email 之類的資料格式驗證都可以做到,這邊就以 Datetime 來做個範例
- 首先是 Schema 的撰寫
scalar DateTime
- 然後是程式的實作,其實蠻好理解的,就是在各個情況下的 parser 撰寫
@Configuration
public class DateTimeScalarConfig {
@Bean
public GraphQLScalarType dateTimeScalarBean() {
return GraphQLScalarType.newScalar()
.name("DateTime")
.description("Java LocalDateTime as scalar.")
.coercing(new Coercing<LocalDateTime, String>() {
@Override
public String serialize(final Object dataFetcherResult) {
if (dataFetcherResult instanceof LocalDateTime) {
return ((LocalDateTime) dataFetcherResult)
.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
} else {
throw new CoercingSerializeException("Expected a LocalDateTime object.");
}
}
@Override
public LocalDateTime parseValue(final Object input) {
try {
if (input instanceof String) {
return LocalDateTime.parse((String) input,
DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
} else {
throw new CoercingParseValueException("Expected a String");
}
} catch (DateTimeParseException e) {
throw new CoercingParseValueException(String.format("Not a valid dateTime: '%s'.", input), e
);
}
}
@Override
public LocalDateTime parseLiteral(final Object input) {
if (input instanceof StringValue) {
try {
return LocalDateTime.parse(((StringValue) input).getValue(),DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
} catch (DateTimeParseException e) {
throw new CoercingParseLiteralException(e);
}
} else {
throw new CoercingParseLiteralException("Expected a StringValue.");
}
}
}).build();
}
}
-
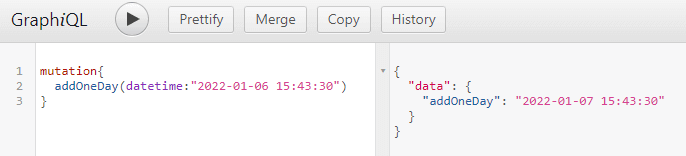
寫個簡單的 Mutation 來測試
-
Schema
type Mutation{
addOneDay(datetime: DateTime): DateTime
}
- Jave
public LocalDateTime addOneDay(LocalDateTime dateTime) {
return dateTime.plusDays(1);
}
- 結果
而 graphql-java-kickstart 也有幫忙實作一些客製化的 Scalar Type,包含以下
BigDecimal, BigInteger, Byte, Char, Date , DateTime, JSON, Locale, Long, NegativeFloat, NegativeInt, NonNegativeFloat, NonNegativeInt , NonPositiveFloat, NonPositiveInt, Object, PositiveFloat, PositiveInt, Short, Time, Url
只要在 application.yaml 中加入設定並在 schema 中定義就可以啟用
graphql:
extended-scalars: BigDecimal, Date
scalar BigDecimal
scalar Date
結語
Mutation 定義上用來做資料的修改,不過實質意義上跟 HttpRequest 的 Method 差不多,實際意義還是端看 Server 如何實作的,有遇過將 CRUD 全部放在 Query 的,而 Scalar Type 的客製化處理雖然方便,但能套用的部分其實也有限,只是用來做第一步的資料驗證,以及給前端看到 Schema 能更了解該傳遞什麼資料